准备启动介质
Fedora 映像是“混合 ISO”,可用于创建带有光盘和 USB 磁盘的安装介质,以便在 BIOS 和 UEFI 系统上启动。
Fedora Media Writer
Fedora Media Writer 已大幅改进,现在是官方的、经过测试的、受支持的启动介质制作方法。Fedora Media Writer 支持 Linux、macOS 和 Windows。它是制作可启动 USB 介质以安装 Fedora(或其他操作系统)的简便方法。强烈建议使用[application]Fedora Media Writer,尽管其他 USB 介质制作软件也可以。
Fedora Media Writer 的一些新功能包括:Fedora 工作站和服务器版可通过主选单的选项方便快捷地选择。如果您选择 自定义镜像 按钮,还可以有更多选择。这将提供各种 Fedora 定制版,例如 Xfce 或 Mate。
从历史上看,通用 USB 创建工具(如 Unetbootin )是一种从用于光学介质的 ISO 创建 USB 安装程序的流行方法。它们通常通过从映像中提取文件在 USB 驱动器上创建文件系统,并将 syslinux 引导加载程序写入设备。
这些方法绕过了 Fedora 映像中内置的引导加载程序配置,这些配置是预先分区的,旨在在启用了安全启动的 UEFI 系统和 BIOS 系统上启动,因此它们不会产生与 Fedora 映像一致的结果,尤其是在 UEFI 系统上。
最好的结果是由使用直接写入方法并且不修改 Fedora 映像的实用程序产生的。
|
在将映像写入设备之前,请务必三思而后行。本文中介绍的媒体创建方法是破坏性的。 在此过程中,U 盘上的所有数据都将被删除,因此请确保备份 U 盘上的数据。仔细检查您是否选择了正确的设备来写入映像! |
安装和运行 Fedora 启动盘写入工具
在 Fedora 上
在 Fedora 25 或更高版本中,Fedora Media Writer 在默认软件源中可用。您可以使用 dnf 安装该软件包。
-
如需安装 Fedora Media Writer,请使用:
$ sudo dnf install mediawriter -
运行应用 Fedora Media Writer:
$ mediawriter或者在 Gnome 3 中选择 活动 ,然后点击 Fedora Media Writer.
在其他 Linux 发行版上
在各种 Linux 发行版上安装 Fedora Media Writer 的最佳方法是使用预置的 Flatpak 软件包。该软件包可从 Flatpak 官方软件仓库 Flathub.org 获取。
-
要在 Linux 系统上安装 Flatpak,请遵循 Flatpak文档 页面上的指南。
-
运行软件:
$ sudo mediawriter
在 Windows 上
-
从 GetFedora.org 下载最新的 Windows 安装程序文件。服务器会自动检测正在运行的系统,并为您的 Windows 版本提供正确的安装文件。
-
通过双击安装程序运行安装,然后继续执行设置向导。该向导允许您自定义软件的安装(如果您愿意)。
-
通过单击启动器运行应用程序。
在 Windows 8 和 10 中,Fedora Media Writer 启动器将放置在 F 下的 所有应用 菜单中。在 Windows 10 中,您只需在任务栏的搜索框中键入 Fedora Media Writer。
在 macOS 上
-
从 GetFedora.org 下载最新的Mac磁盘映像(软件包扩展名为 .dmg)。服务器会自动检测运行的系统,并为您的 macOS 提供正确的软件包。
-
打开
.dmg文件,在点击 Fedora Media Writer 程序的同时按住 Ctrl 键。 -
在弹出菜单中点击 “打开”。
-
如果出现确认对话框,点击其中的 “打开” 按钮。
将 ISO 映像写入 USB 介质。
-
选择您希望为其制作可启动 USB 驱动器的 Fedora 版本。
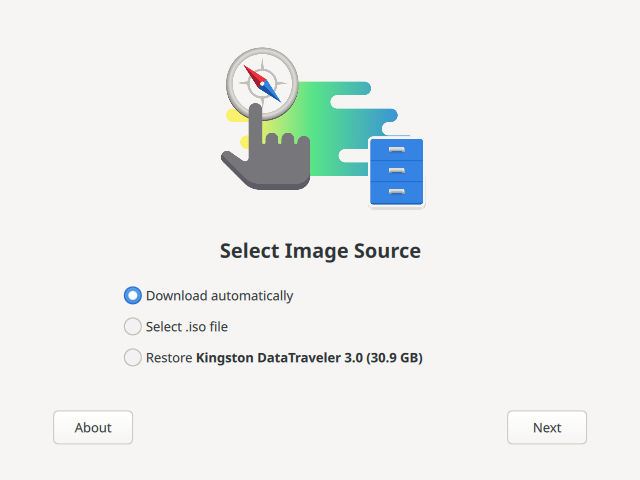 Figure 1. Fedora 启动盘写入工具主屏幕:选择您的 Fedora 版本
Figure 1. Fedora 启动盘写入工具主屏幕:选择您的 Fedora 版本主选项可让您选从默认的 Fedora 工作站版 或 服务器版 选择其一。在下载映像和创建 USB 之前,Fedora Media Writer 会显示有关版本的更多详细信息。如果选择 其他发行版 ,您可以选择不同的架构。
-
选择 “创建 Live USB” 以继续。
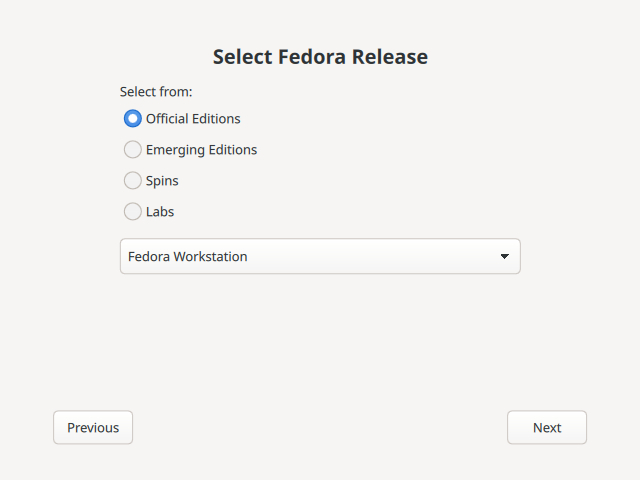 Figure 2. Fedora 启动盘写入工具发行版信息
Figure 2. Fedora 启动盘写入工具发行版信息Fedora Media Writer 会自动为您下载 ISO。如果您之前下载过 ISO 并将其放在 下载 目录中,它将立即可供使用。
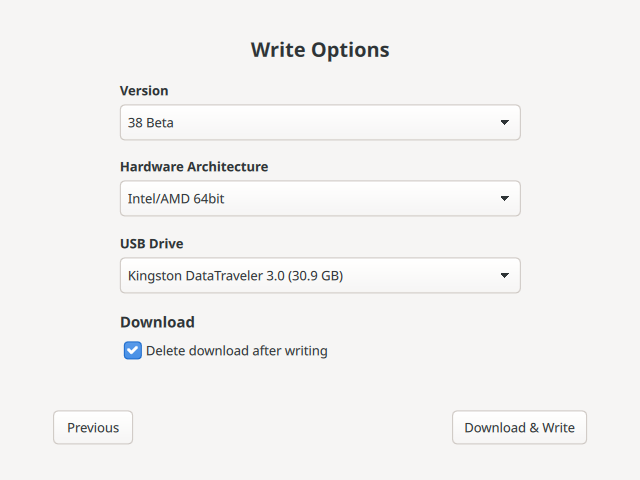 Figure 3. Fedora Media Writer 自动下载
Figure 3. Fedora Media Writer 自动下载 -
插入要在其上创建可启动媒体的 USB 驱动器。
-
要将映像写入介质,请单击红色的 写入磁盘按钮。
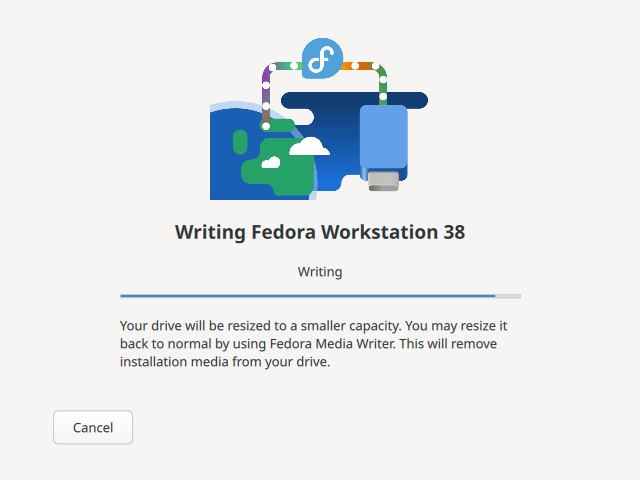 Figure 4. Fedora Media Writer 写入U盘
Figure 4. Fedora Media Writer 写入U盘
创建实时 USB 的其他方法
强烈建议大家使用 Fedora Media Writer,因为它提供了一种可靠的方法来创建用于安装 Fedora 的Live U 盘。
不过,一些有经验的用户可能更愿意手动完成创建过程。如果您决定这样做,就必须下载安装映像,并使用应用程序将其写入 U 盘。
|
如果您已手动下载并验证了安装映像,仍可使用 Fedora Media Writer 将其写入 U 盘。 |
下载启动和安装映像
Fedora 项目针对一些特定的使用情况提供不同的版本。请选择最适合您的 Fedora 版本。您也可以在 Fedora 安装完成后对其进行自定义,或者使用 创建一个Kickstart文件 所描述的Kickstart文件来创建您自己的 Fedora 版本。
Kickstart 安装要求使用 网络安装 介质类型或 PXE 等直接安装启动的方法;Live映像不支持 kickstart。
了解更多有关 Fedora 工作站、Fedora 云、Fedora 服务器版和可用介质类型的信息,请参阅 下载 Fedora。
您还可以在 https://spins.fedoraproject.org中选择 Fedora 定制版,其中包含您最喜爱的替代桌面环境或用于专门任务的工具。
正在验证已下载的镜像
由于传输错误或其他问题可能会损坏您下载的 Fedora 映像,因此验证文件的完整性非常重要。镜像创建后,会对文件执行一个操作,使用复杂的数学算法生成一个称为 校验和 的值。该操作非常复杂,以至于对原始文件的 *任何改动*都会产生不同的校验和。
By calculating the image’s checksum on your own computer and comparing it to the original checksum, you can verify the image has not been tampered with or corrupted. The original checksum values are provided at https://getfedora.org/security/, and are gpg signed to demonstrate their integrity.
Verifying checksums on Windows systems
-
Download the Fedora image of your choice from https://getfedora.org/ and the corresponding checksum file from https://getfedora.org/security/
-
Open a powershell session.
-
Change to the directory containing the downloaded files.
> cd $HOME\Downloads\ > ls Directory: C:\Users\Pete\Downloads Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- -a--- 11/25/2014 12:39 PM 272 Fedora-Server-21-x86_64-CHECKSUM -a--- 11/25/2014 12:39 PM 2047868928 Fedora-Server-DVD-x86_64-21.iso
-
Load the resources required to calculate the checksum.
> $image = "Fedora-Server-DVD-x86_64-21.iso" > $checksum_file = "Fedora-Server-21-x86_64-CHECKSUM" > $sha256 = New-Object -TypeName System.Security.Cryptography.sha256CryptoServiceProvider > $expected_checksum = ((Get-Content $checksum_file | Select-String -Pattern $image) -split " ")[0].ToLower()
-
Calculate the downloaded image’s checksum. This will take a while!
> $download_checksum = [System.BitConverter]::ToString($sha256.ComputeHash([System.IO.File]::ReadAllBytes("$PWD\$image"))).ToLower() -replace '-', '' -
Compare the calculated checksum to the expected checksum.
> echo "Download Checksum: $download_checksum" > echo "Expected Checksum: $expected_checksum" > if ( $download_checksum -eq "$expected_checksum" ) { echo "Checksum test passed!" } else { echo "Checksum test failed." }
Verifying checksums on Linux and macOS systems
-
Download the Fedora image of your choice from https://fedoraproject.org/get-fedora and the corresponding checksum file from https://getfedora.org/security/
-
Open a terminal window, and navigate to the directory with the downloaded files.
$ cd ~/Downloads -
Use the appropriate utility to verify the image checksum.
-
For Linux:
$ sha256sum -c *CHECKSUM
-
For macOS:
$ grep '^SHA256' *-CHECKSUM | awk -F '[()=]' '{ print $4 " " $2 }' | shasum -a 256 -c
-
Writing the images to USB media
Creating USB media with GNOME Disks
-
On a system with GNOME, or with the gnome-disk-utility package installed, open
Disksusing the system menu. -
Click your USB device in the left column.
-
Click the menu icon in the upper right corner of the window, and choose the
Restore Disk Imageoption. -
Navigate to your image file and click
Start Restoring. After a few minutes, it will report the process is complete and your installation media will be ready to use.
Creating USB Media on the Linux command line
-
Open a terminal window and insert the usb drive.
-
Find the
device nodeassigned to the drive. In the example below, the drive is givensdd.$ dmesg|tail [288954.686557] usb 2-1.8: New USB device strings: Mfr=0, Product=1, SerialNumber=2 [288954.686559] usb 2-1.8: Product: USB Storage [288954.686562] usb 2-1.8: SerialNumber: 000000009225 [288954.712590] usb-storage 2-1.8:1.0: USB Mass Storage device detected [288954.712687] scsi host6: usb-storage 2-1.8:1.0 [288954.712809] usbcore: registered new interface driver usb-storage [288954.716682] usbcore: registered new interface driver uas [288955.717140] scsi 6:0:0:0: Direct-Access Generic STORAGE DEVICE 9228 PQ: 0 ANSI: 0 [288955.717745] sd 6:0:0:0: Attached scsi generic sg4 type 0 [288961.876382] sd 6:0:0:0: sdd Attached SCSI removable disk -
Use the dd utility to write the image.
# dd if=/path/to/Fedora-Live-Security-x86_64-21.iso of=/dev/sdd
Pay extreme attention to the source (
if=) and target (of=) device. Theddcommand destroys all data on the target device. If you made a mistake, you could lose important data.
Creating a Boot CD or DVD
In addition to creating a bootable USB flash drive, you can also use the provided ISO images to create bootable optical media (a CD or DVD). This approach may be necessary when installing Fedora on an older system which cannot boot from USB.
|
The exact steps you need to take to burn a bootable CD or DVD from an ISO image will vary depending on what disc burning software you use. This procedure only offers a general overview. |
-
Insert a blank CD or DVD into your system’s CD or DVD burner.
-
Open your system’s burning software - for example, Brasero on Fedora systems with GNOME desktop environment, or Nero on Windows systems. In the software’s main menu, find an option which lets you burn an ISO image to a disc. For example, in Brasero, this option is
Burn imagein the main menu on the left side of the window. -
When prompted, select the ISO image of Fedora to be burned, and the CD or DVD burner with a blank disc inside (if you have more than one drive).
-
Confirm your selection, and wait for the disc to be burned.
Want to help? Learn how to contribute to Fedora Docs ›